Description
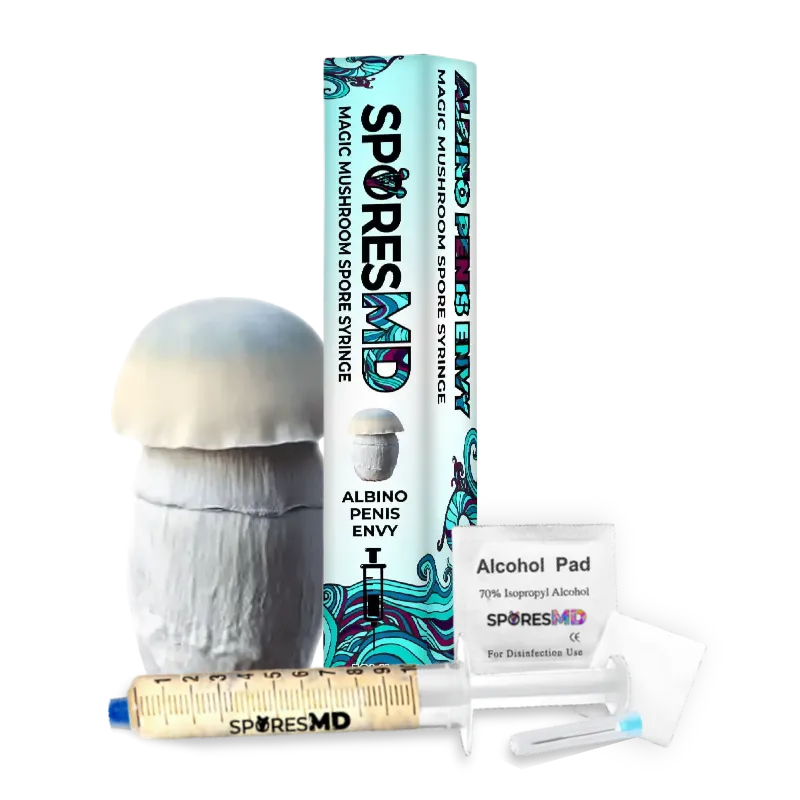
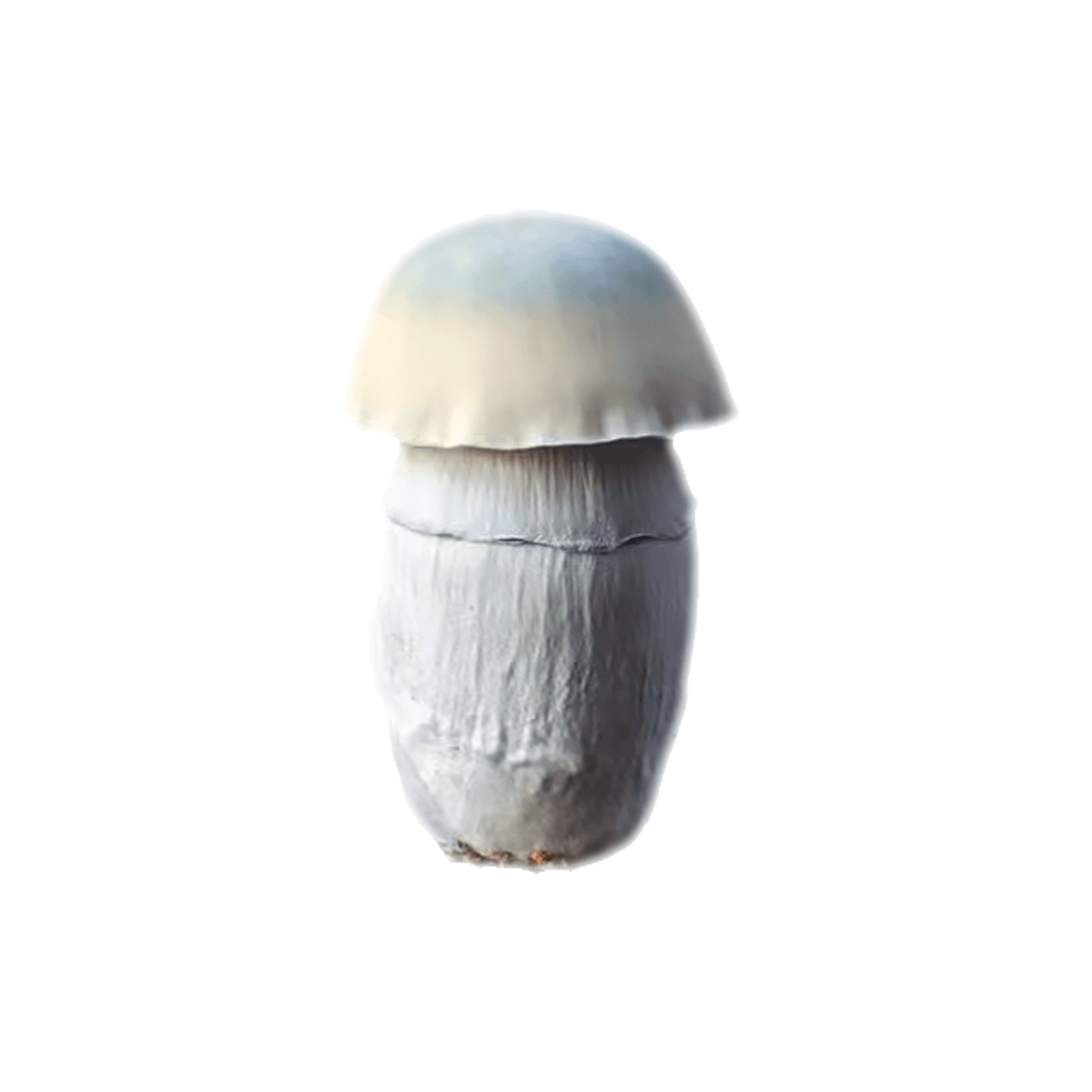
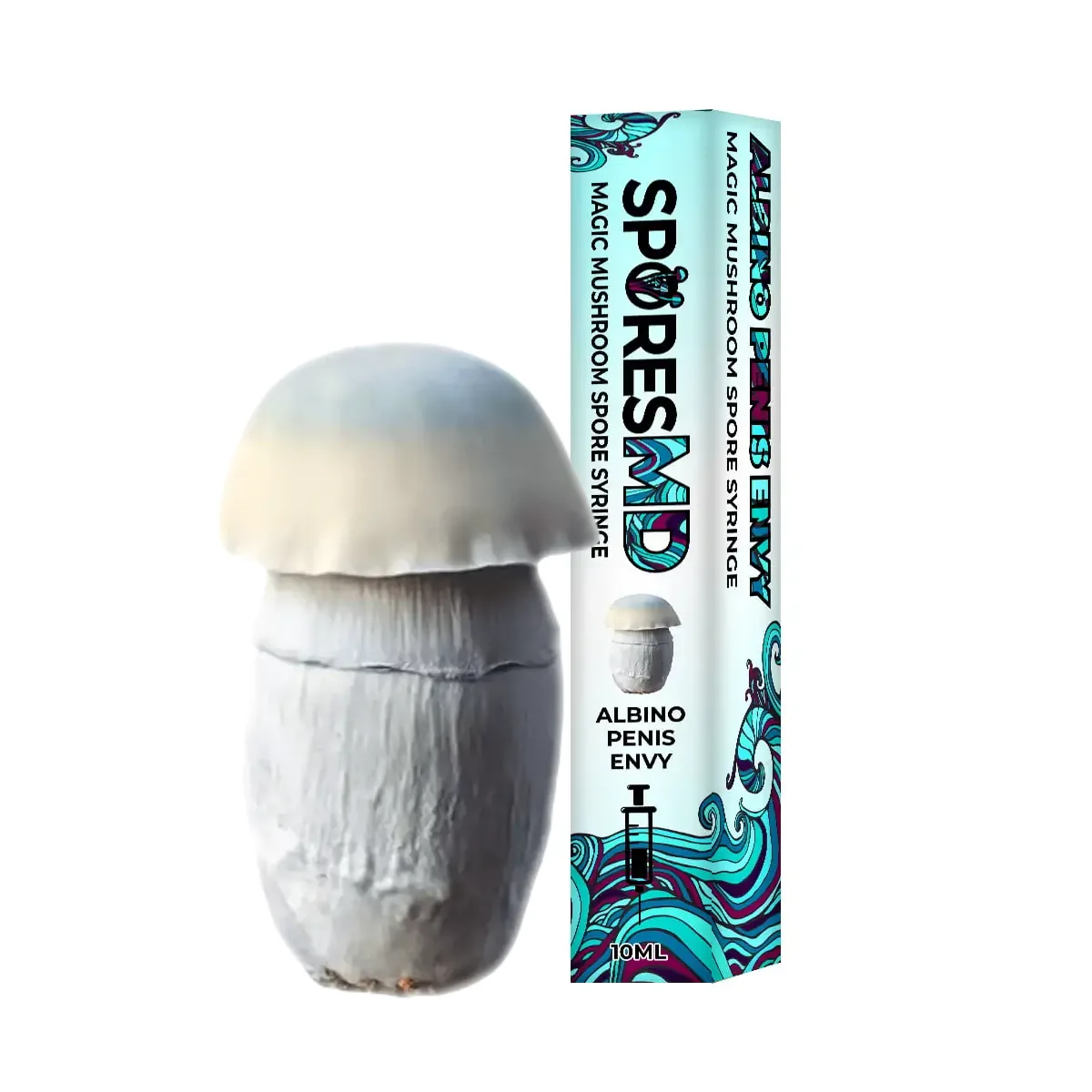
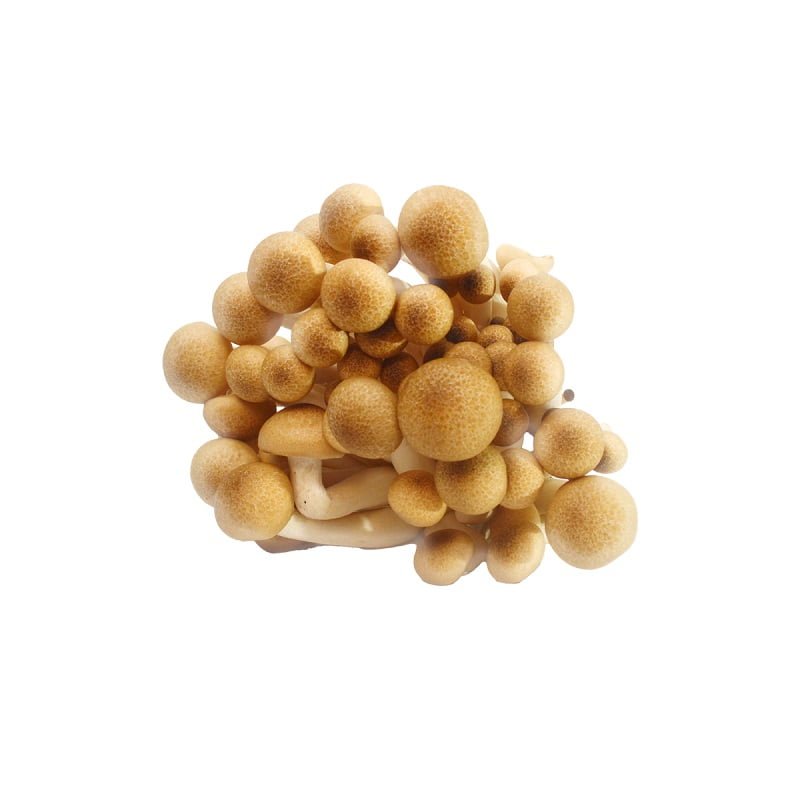
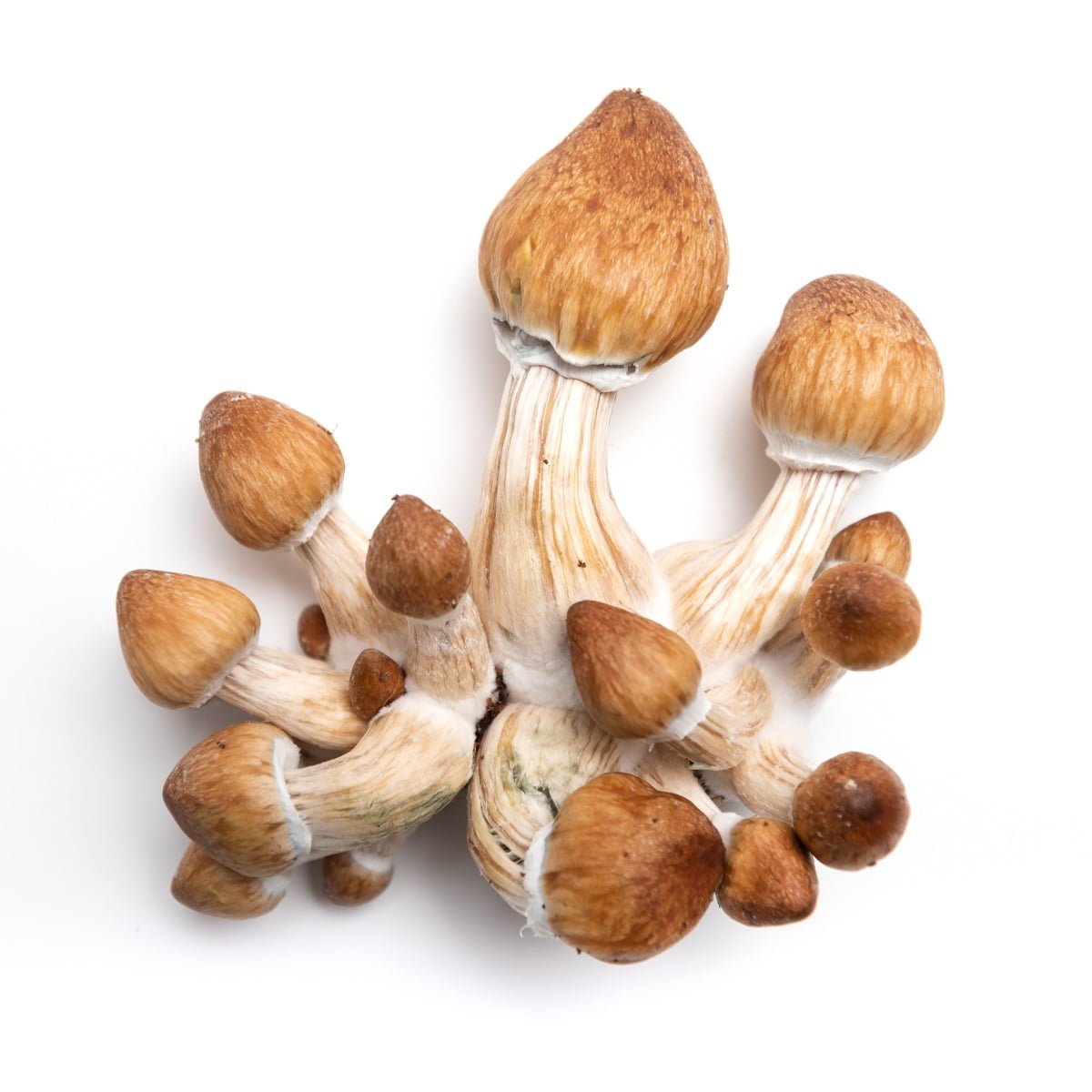
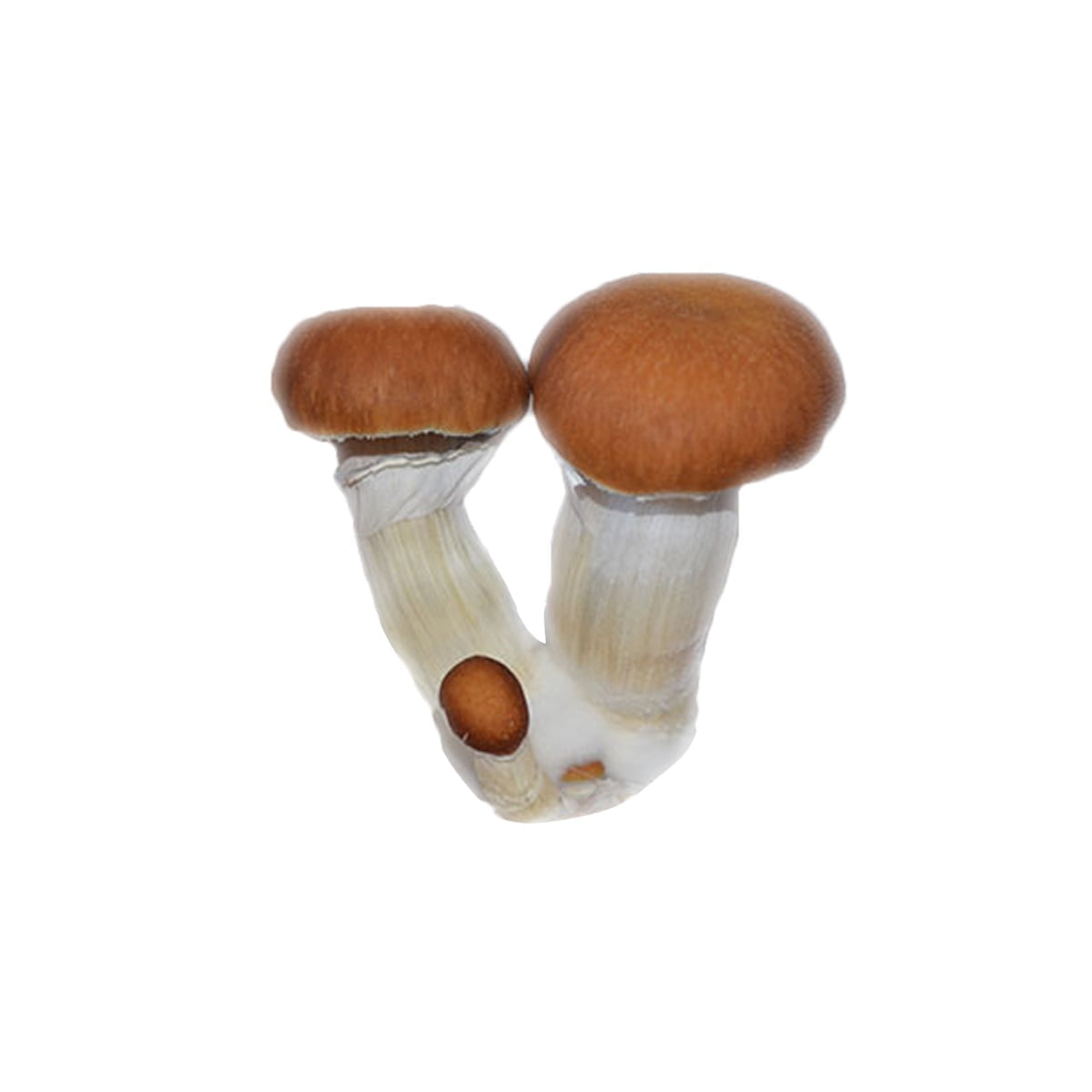
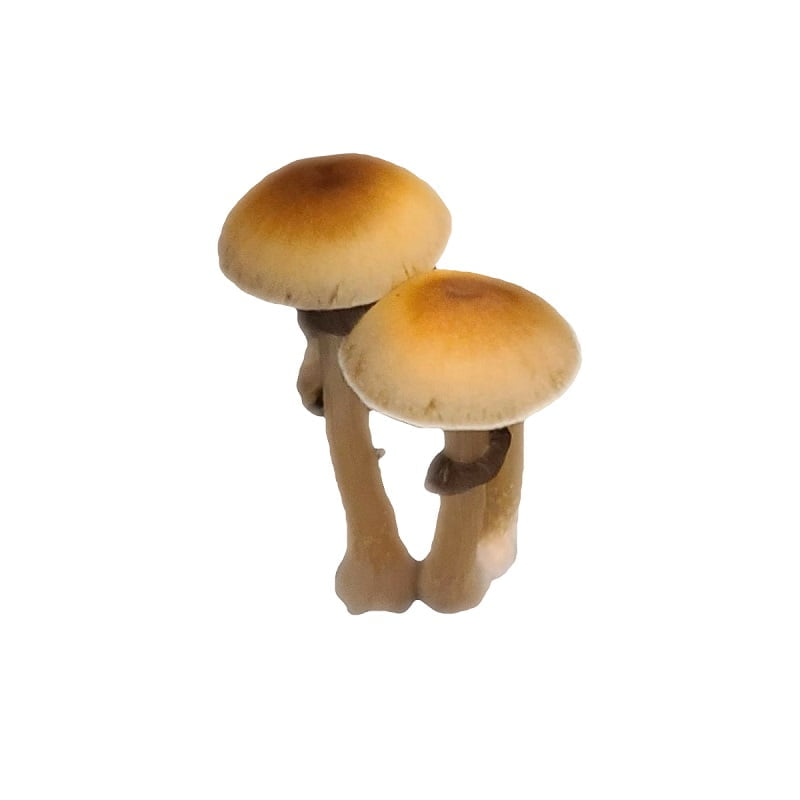
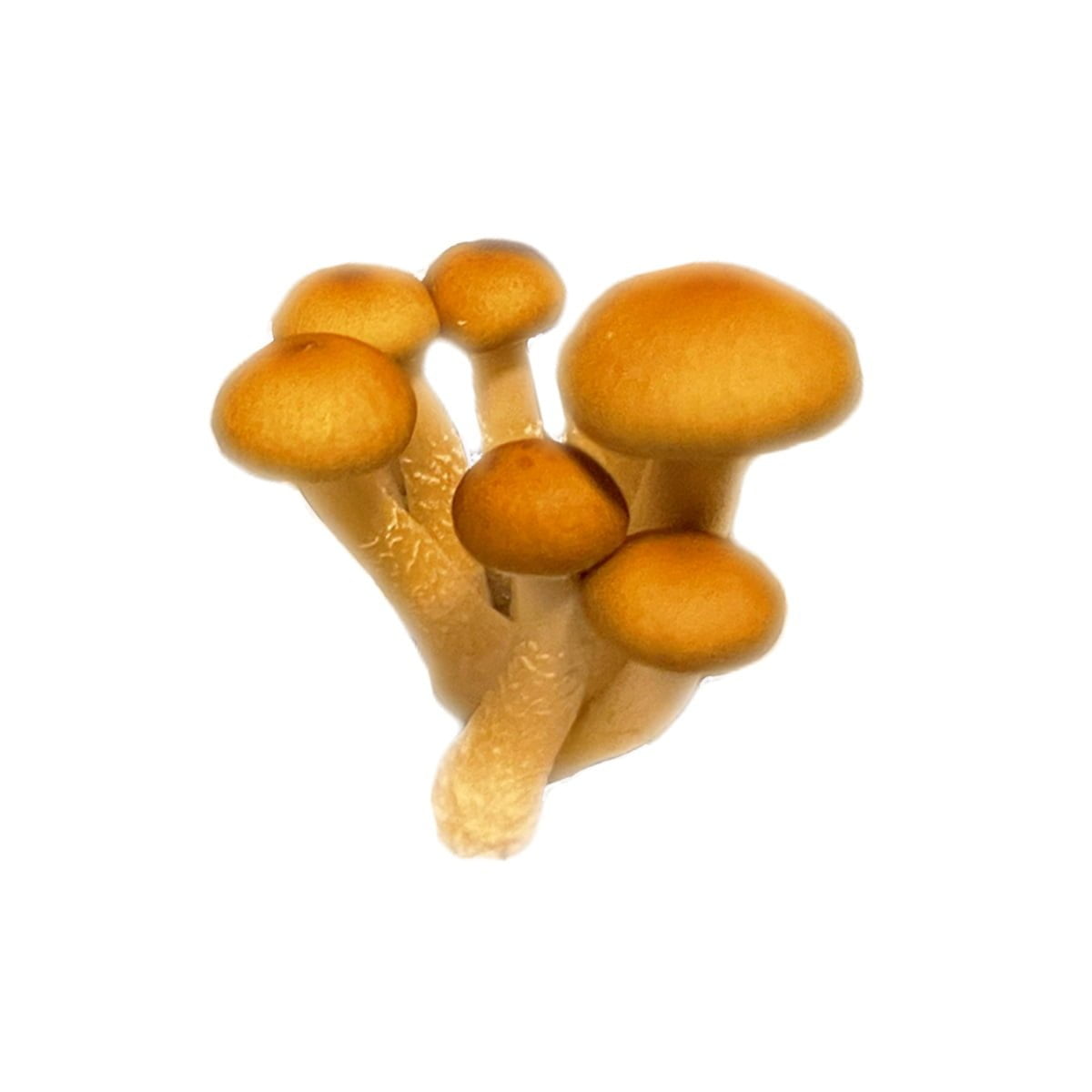
The Albino Penis Envy (APE) variant of Psilocybe cubensis stands out within the mycological landscape, drawing attention for its unique genetic composition and the rich historical narrative surrounding its lineage. Originating from the well-known Penis Envy (PE) strain, believed to be discovered or developed by the renowned ethnobotanist Terence McKenna, the APE variant is notable for its distinct albino trait, a rare occurrence in Psilocybe cubensis varieties. This albinism results in a striking visual appearance, with the mushroom exhibiting a pale or white hue due to the absence of typical pigmentation.
Mycological enthusiasts and researchers are captivated by the APE strain’s distinct morphological features, especially under microscopic examination. The caps and stems of the APE display a unique translucency, setting it apart from other variants. The robust and thick-stemmed structure, a characteristic inherited from its PE progenitor, is complemented by smaller, often bulbous caps, presenting a fascinating subject for those exploring the physical diversity within the Psilocybe cubensis species.
The genetic makeup of the Albino Penis Envy strain is a pivotal area of study in fungal genetics and mycology. The manifestation of albinism in this variant provides key insights into genetic mutations and variations within the species. Additionally, the APE’s slower growth rate and distinctive developmental patterns compared to other strains contribute valuable data to the understanding of fungal life cycles and morphological diversity.
In summary, the Albino Penis Envy variant of Psilocybe cubensis represents a fascinating convergence of history, science, and mycology. Its distinctive physical characteristics and unique genetic attributes make it an invaluable subject for educational and research-focused endeavors. The APE strain’s standing in the mycological community underscores the intricate and ever-evolving nature of fungal genetics, as well as the enduring interest in the study and understanding of psilocybe cubensis mushrooms.